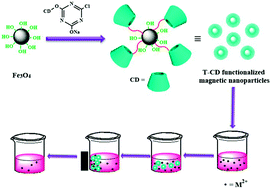
In this contribution, novel nano-adsorbent, triazinyl-β-cyclodextrin modified magnetic nanoparticles (T-β-CD–MNPs) were fabricated for the removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions by reacting mono-chlorotriazinyl-β-cyclodextrin (T-β-CD) with magnetite Fe3O4 nanoparticles (MNPs) via the nucleophilic substitution of the chloride leaving group of T-β-CD by the attacking hydroxyl group of the MNPs. T-β-CD–MNPs exhibit excellent removal ability for heavy metal ions (Pb2+, Cu2+, Zn2+ and Co2+). The grafted T-β-CD on the MNP surface contributes to an improvement of the adsorption capacity due to the strong abilities of the multiple hydroxyl and azinyl nitrogen groups in T-β-CD to adsorb metal ions. They also exhibited a relatively good saturation magnetization (67 emu g−1), which allowed their highly-efficient magnetic separation from wastewater. Equilibrium data for metal ion adsorption fit well with the Langmuir isotherm model with maximum adsorption capacities of 105.38, 58.44, 51.30 and 33.33 mg g−1 for Pb2+, Cu2+, Zn2+ and Co2+, which is larger than MNPs that had been modified by other natural compounds. The excellent adsorption capacity of T-β-CD–MNPs, together with other advantages such as reusability, easy separation, environmentally friendly composition, and their simple preparation method, make them suitable adsorbents for the removal of heavy metal ions from environmental and industrial waste.